The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced that the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) will be launched on Saturday to send two satellites that are the property of Singapore into space.
The launch pad for the PSLV C55 is located at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre on Sriharikota island in southeast India. The launch is slated to take place at 14:19 local time.
The PSLV is a four-stage medium-class launch vehicle that can send an object into different orbits, including about 1.7 tonnes into a sun-synchronous polar orbit and 1.4 tonnes into a geo transfer orbit.
TeLEOS-2
DSTA (which represents the Singapore government) and ST Engineering (Satellite Systems) are developing the TeLEOS-2 satellite. Once it is set up and working, it will be used to meet the needs of different government departments in Singapore for satellite imagery.

The SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) package on TeLEOS-2. TeLEOS-2 will be able to take pictures with a full polarimetric resolution of 1 m, and it will be able to do this in any weather, day or night. It will have a 500 GB recorder on board for saving data and an 800 Mbps downlink, a fast way to send data back to Earth.
ISRO put TeLEOS-1, Singapore’s first commercial Earth Observation Satellite, into low Earth orbit in 2015 for remote sensing. ISRO has sent nine satellites into space for Singapore so far.
LUMELITE-4
Also, an experimental cubesat called LUMELITE-4 will be sent into space. It is made by the Singapore National University and the Singapore Agency for Science, Technology, and Research. The 16 kg craft will show how a new high-speed data transfer system works in space. This is a system that Singapore wants to use to improve the safety of ships’ navigation systems.
PSLV 4th Stage – POEM-2
The rocket’s fourth stage will stay in space and be used as a research platform for scientists. In total, seven tests are going to be done.
The used PS4 stage of the launch vehicle is used by the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module, also known as the POEM, as a platform in orbit to conduct scientific experiments with payloads that do not separate. The ISRO, Bellatrix, Dhruva Space, and the Indian Institute of Astrophysics are the organisations that own the various instruments.
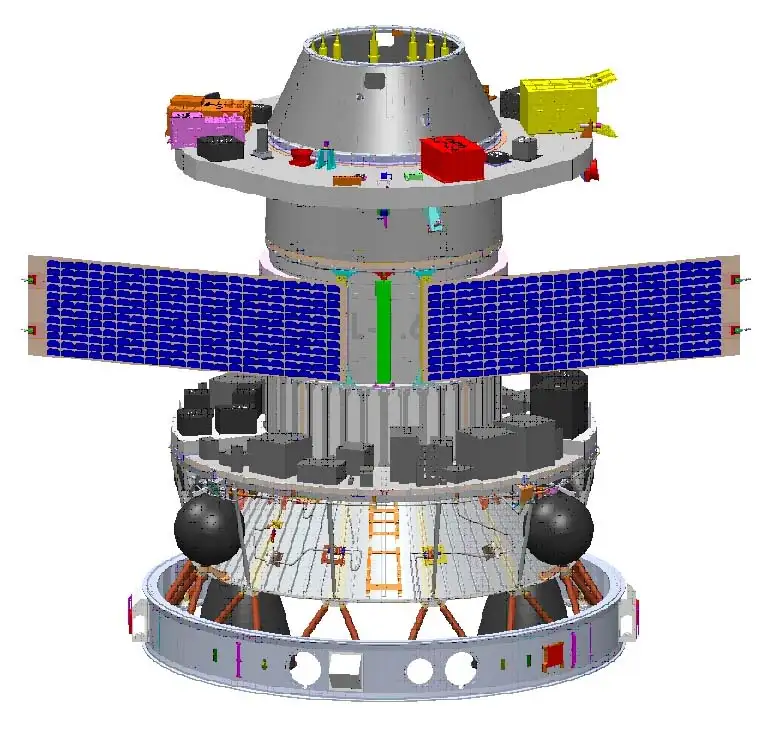
The payloads include PSLV In orbitaL Obc and Thermals (PiLOT), an OBC package and an Advanced Retarding Potential analyser for Ionospheric Studies (ARIS-2) experiment from IIST, HET-based ARKA200 Electric Propulsion System from Bellatrix, DSOD-3U and DSOD-6U deployer units along with DSOL-Transceiver in S- & X- bands from Dhruva Space; and Starberry Sense Payload from Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IAP).
The Indian Institute of Astrophysics, which is launching the Starberry into space, stated that the low-cost device was designed to precisely identify and measure the positions of stars in outer space. Built from commercial off-the-shelf components and once tested in orbit, it will be a fantastic option for future space missions to determine where they are pointed, according to a tweet from the IIA.
POEM was first launched in 2022. POEM contains a dedicated Navigation Guidance and Control (NGC) system for attitude stabilisation, which controls the orientation of any aerospace vehicle within permitted limits. The NGC serves as the platform’s brain to regulate it precisely. POEM carried six payloads, two of which were from Indian Space Startups, Digantara and Dhruva Space and were facilitated by IN-SPAC and NSIL. POEM was powered by solar panels affixed to the PS4 tank and a Lithium-ion battery. It uses four Sun Sensors, a Magnetometer, Gyros, and NavIC to navigate. In addition, it was equipped with control thrusters with Helium gas storage. It is equipped with telecommand capabilities.
PSLV-CA
ISRO debuted PSLV-CA on April 23, 2007. The abbreviation for “Core Alone” is “CA.” PSLV-CA was able to carry out 15 launches, all of which were successful. The CA model does not include any of the PSLV standard configuration’s six strap-on boosters since this component is not included in the CA model. Compared to the conventional version, the CA variant’s fourth stage requires 400 kg less fuel to function properly. It can launch 1,100 kg into a Sun-synchronous orbit that is 622 kilometres away.
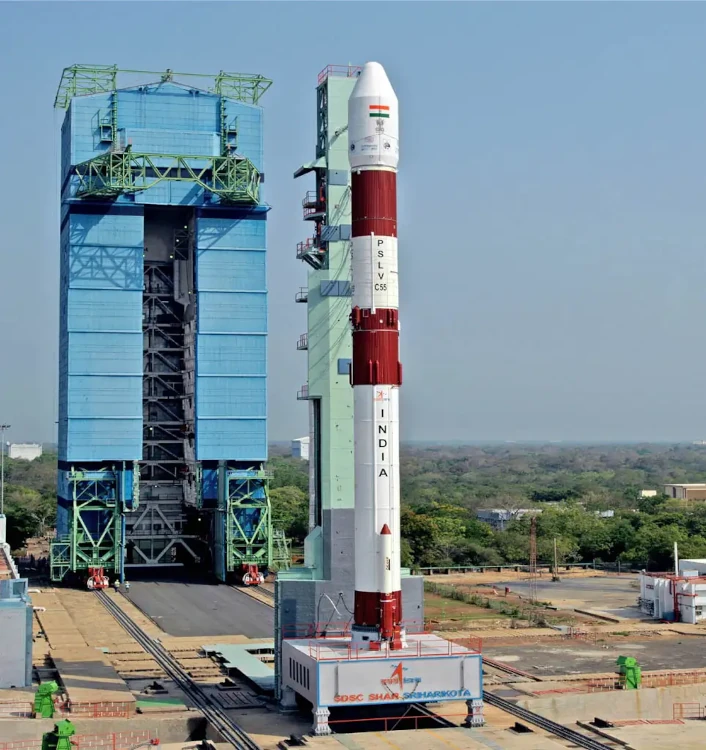

ISRO is launching for the third time this year, and they have used different launch vehicles all three times. The first launch was in February with the new Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
In March, the country’s largest rocket, LVM3, was used for the second launch. It sent 36 OneWeb satellites into space on a strictly business mission.






